User Guide
- Introduction
- About this Guide
- Quick Start
-
Features
- Housing Management
- Data Management
- Student Management
-
General
- Listing all bin items :
bin - Restoring a bin item :
restore - Set bin expiry time :
set-bin-expiry - Listing all aliases :
aliases - Adding an alias :
alias - Deleting an alias :
dealias - Asking for help as a first time user :
help - Checking the syntax for a command:
help - Clearing all entries :
clear - Undo previous command :
undo - Redo previous undo command :
redo - List previously entered nonempty commands :
history - Exiting ResiReg :
exit - View students and rooms side by side:
toggle-split - View students and rooms in separate tabs:
toggle-split
- Listing all bin items :
- FAQ
- Command Summary
Introduction
ResiReg (Residential Regulation) is a productivity app designed to help admin staff at Residential Colleges (RCs) in NUS with their daily tasks.
ResiReg has the following main features:
- Manage records of students.
- Manage records of rooms.
- Manage allocations of students to rooms in the College.
ResiReg is optimised for admin staff who are fast typists who are used to a Command Line Interface, and prefer typing over other means of input. It comes with:
- A Command Line Interface (CLI) which allows you to access all ResiReg features by typing.
- A Graphical User Interface (GUI) that displays the information you need.
ResiReg is always a work in progress (even after this semester!). Here is its current look. Stay tuned for our progress!
About this Guide
Basic Information
This User Guide explains how you can use ResiReg to manage tasks at Residential Colleges.
You may refer to Quick Start for a short tutorial on how to run ResiReg on your system and use ResiReg’s main features. For a full walkthrough of ResiReg, please refer to Features.
Quick Start
ResiReg runs on Windows, Linux, and OS-X.
- Ensure that Java 11 or above is installed in your computer.
- Download the latest
resireg.jarhere. - Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your ResiReg.
- Double-click the file to start the app. The app window should open in a few seconds.
- Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will display a help message containing a list of available commands, as well as a link to this User Guide. - Some example commands you can try:
-
rooms --vacant: lists all rooms that are vacant. -
allocate si/1 ri/2: allocates the 1st student in the student list to the 2nd room in the room list. -
exit: exits the app.
-
- Refer to “Features” for details of all the commands.
Features
This section explains the format of commands in this User Guide.
- Words in
<angular_brackets>are the parameters to be supplied by the user e.g. indeallocate <student_name>,<student_name>is a parameter which can be used asdeallocate Jet New. - Items in square brackets are optional e.g
<full_name> [-aka <alias>]can be used asJet New -aka JJor asJet New. - Items separated by
orindicates a choice between items, but only one item is to be used at any time e.g.--vacant or --allocatedmeans either the--vacantor the--allocatedflag (but not both) can be used. - Items with
…after them can be used multiple times including zero times, unless otherwise stated.
Housing Management
ResiReg allows you to manage rooms in the Residential College.
Listing and filtering rooms : rooms
Switches to the room tab if it is not already selected and shows a list of rooms in ResiReg, optionally filtered by some criteria.
Format: rooms [--vacant or --allocated] [fl/<floor>]... [n/<room_number>]... [t/<room_type>]...
- If no parameters are given, all rooms are shown.
-
--allocatedshows all rooms that have been allocated to a student, while--vacantshows all vacant rooms. - Rooms can be filtered by multiple criteria. Criteria of the same type (eg. floors) are combined using “or” while criteria of different types are combined using “and”. See the section below for some examples.
Examples:
-
roomsshows all rooms -
rooms fl/11shows all rooms on floor 11. -
rooms --vacant fl/11 fl/12 t/CNshows all vacant rooms of type corridor non-aircon which are on either floor 11 or floor 12.
Adding a room: add-room
Adds a room to ResiReg. The following room details are stored: room floor, room number, room type, and optionally, tags.
Format: add-room fl/<floor> n/<room_number> t/<room_type> [tag/<tag_name>]...
- The floor number must be a positive integer between 1 and 99 inclusive.
- The room number must be a positive integer between 100 and 999 inclusive.
- Room type must be one of the following values:
CA(corridor, aircon),CN(corridor, non-aircon),NA(non-corridor, aircon),NN(non-corridor, non-aircon) - The room will not be added if any piece of required information is missing. An error message will be displayed instead.
Examples:
-
add-room fl/12 n/112 t/CAadds the room #12-112 of type corridor aircon.
Deleting a room: delete-room
Deletes the specified room from ResiReg.
Format: delete-room <index>
- Deletes the room at the specified
index, and moves the room to the bin. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed room list.
Examples:
-
delete-room 1Removes the room at index1from ResiReg.
Editing rooms: edit-room
Edits an existing room in ResiReg.
Format edit-room <index> [fl/<floor>] [n/<room_number>] [t/<room_type>] [tag/<tag_name>]...
- Edits the room at the specified
index. The index refers to the index number shown in the currently displayed room list. - Constraints on floor, room number and room type are specified under
add-room.
Examples:
-
edit-room 1 t/CNChanges the room type of the 1st room toCN.
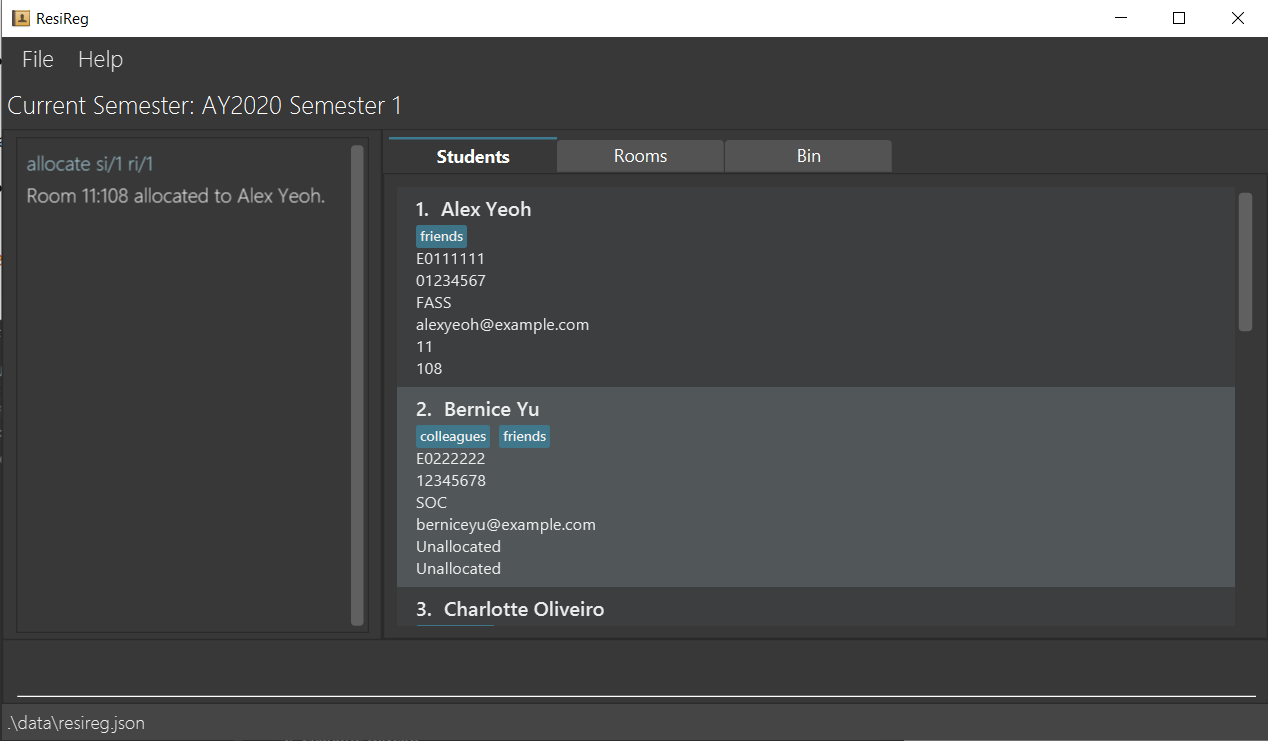
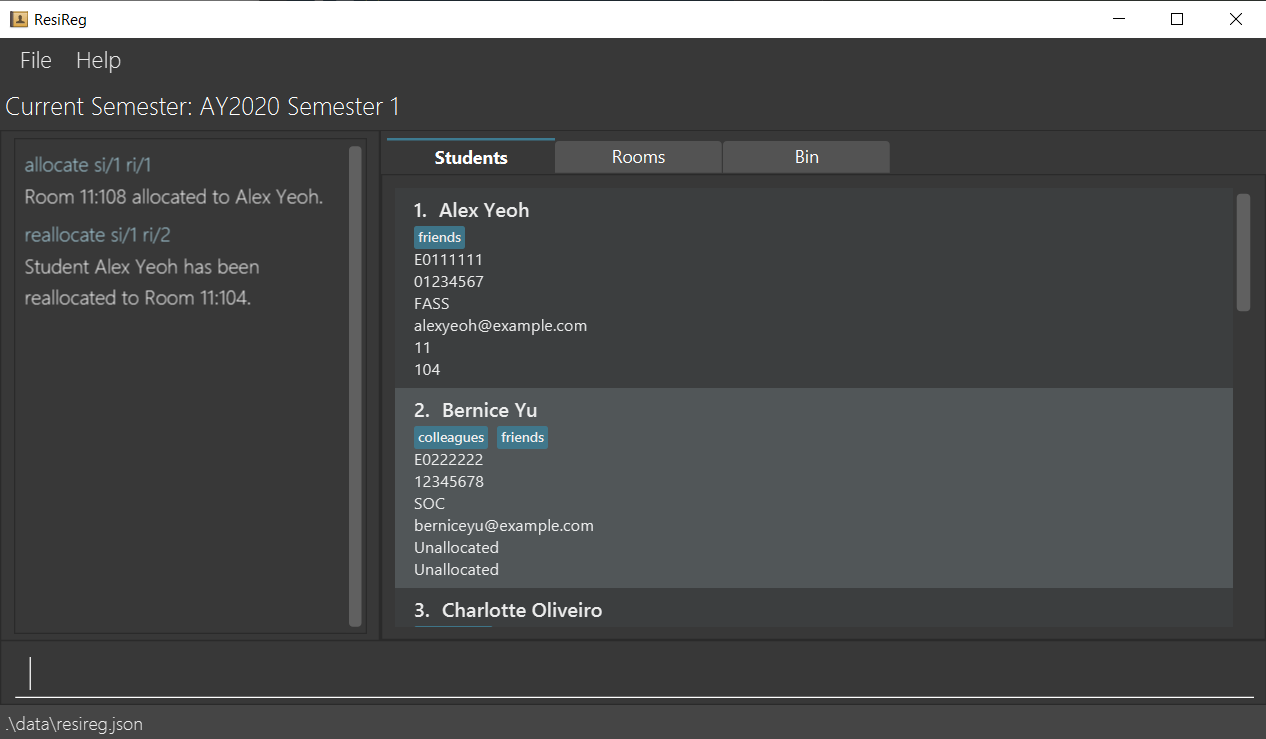
Allocating a room to a student : allocate
Allocates a room to a student i.e denotes that the student currently occupies the room.
Format: allocate ri/<room_index> si/<student_index>
- Allocates a room to the student at the specified
room_indexandstudent_index. Theroom_indexrefers to the index number shown in the displayed rooms list, and thestudent_indexrefers to the index number shown in the displayed student list. Both indices must be positive integers 1, 2, 3, … - Both the student and the room must be unallocated when this command is run. Otherwise, an error message is displayed accordingly.
Examples:
-
allocate ri/1 si/1allocates the room atroom_index1 to the student atstudent_index1.
Before allocation
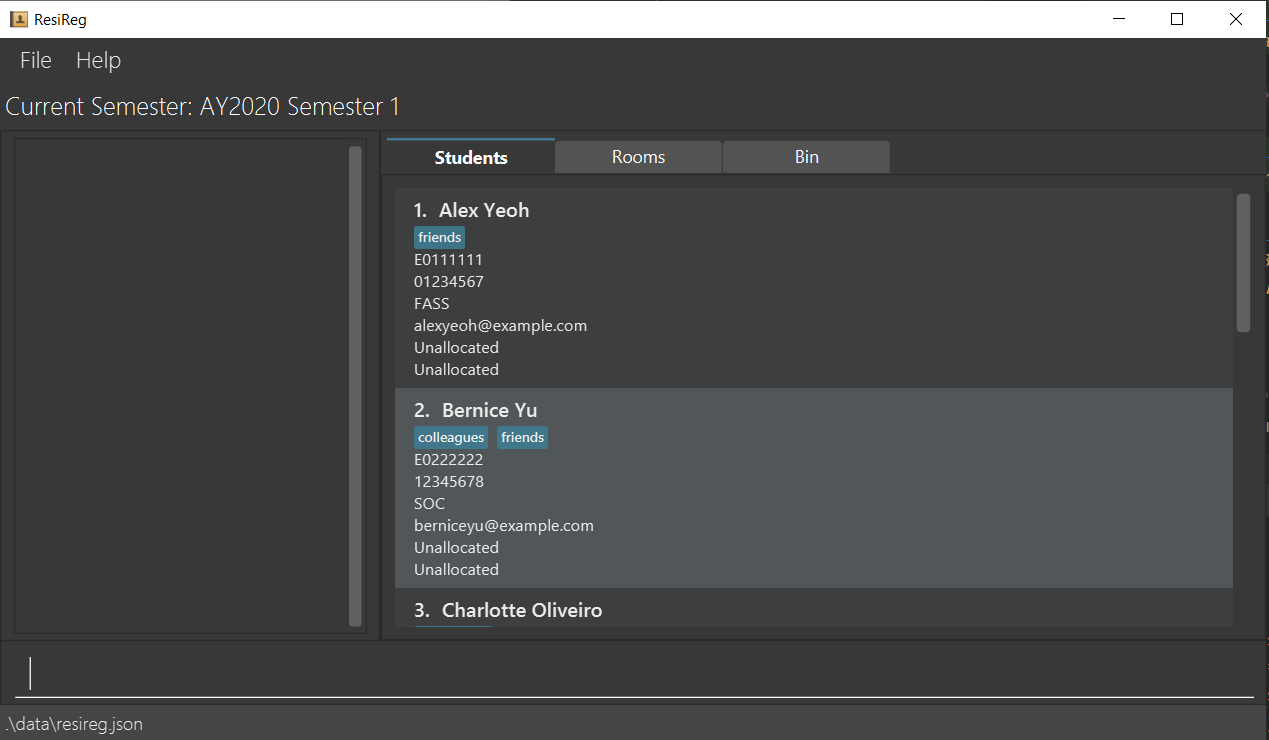
After allocation
Deallocating a room for a student : deallocate
Deallocates a room for a student i.e denotes that the student no longer occupies the room.
Format: deallocate si/<student_index>
- Deallocates a room to the student at the specified
student_index. Thestudent_indexrefers to the index number shown in the displayed students list. Thestudent_indexmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - The student at
student_indexmust have been allocated a room. Otherwise, an error message is displayed.
Examples:
-
deallocate si/1deallocates the room for the student atstudent_index1.
Before deallocation
Refer to After Allocation above.
After deallocation
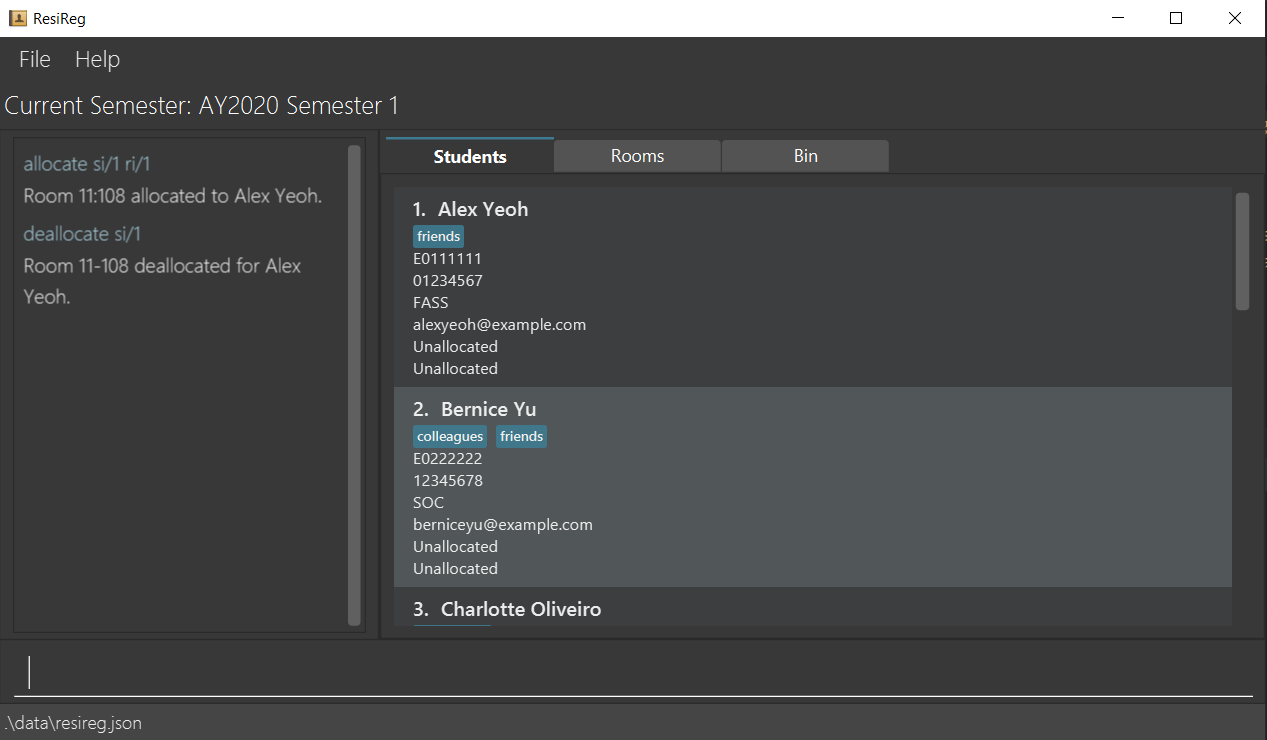
Reallocating a room for a student : reallocate
Reallocates a room for a student, by editing the allocation relating a student to its current room.
Format: reallocate si/<student_index> ri/<room_index>
- Reallocates the room at
room_indexto the student at the specifiedstudent_index. Theroom_indexrefers to the index number shown in the displayed rooms list, and thestudent_indexrefers to the index number shown in the displayed student list. Both indices must be positive integers 1, 2, 3, … - The student at
student_indexmust currently have a room allocation (which is not the specified room). Otherwise, an error message is displayed accordingly. - The room at
room_indexmust currently be vacant. Otherwise, an error message is displayed accordingly.
Examples:
-
reallocate si/1 ri/2edits the allocation of the student with index 1’s current room to the room with index 2.
Before reallocation
Refer to After Allocation above.
After reallocation
Data Management
ResiReg allows you to manage allocations on a per-Semester basis.
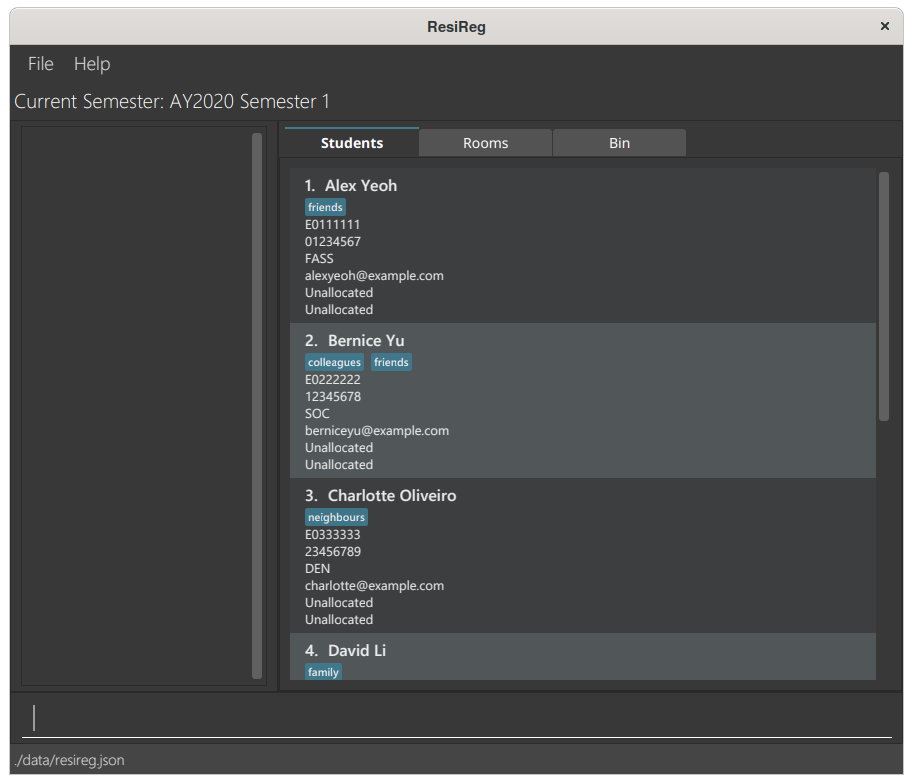
Archiving a Semester: archive
Archives the previous semester’s data into an archival folder, and adjusts the application to operate on the succeeding semester.
Format: archive
- Moves the previous semester’s allocation data to
AY[YEAR]S[SEMESTER]/archive.json. For example, if the previous semester was 2019 Semester 2, the allocation data will be moved toAY2019S2/archive.json. - The rooms and students are still preserved in the system.
- Additional arguments passed to the command are ignored.
Before archival
After archival
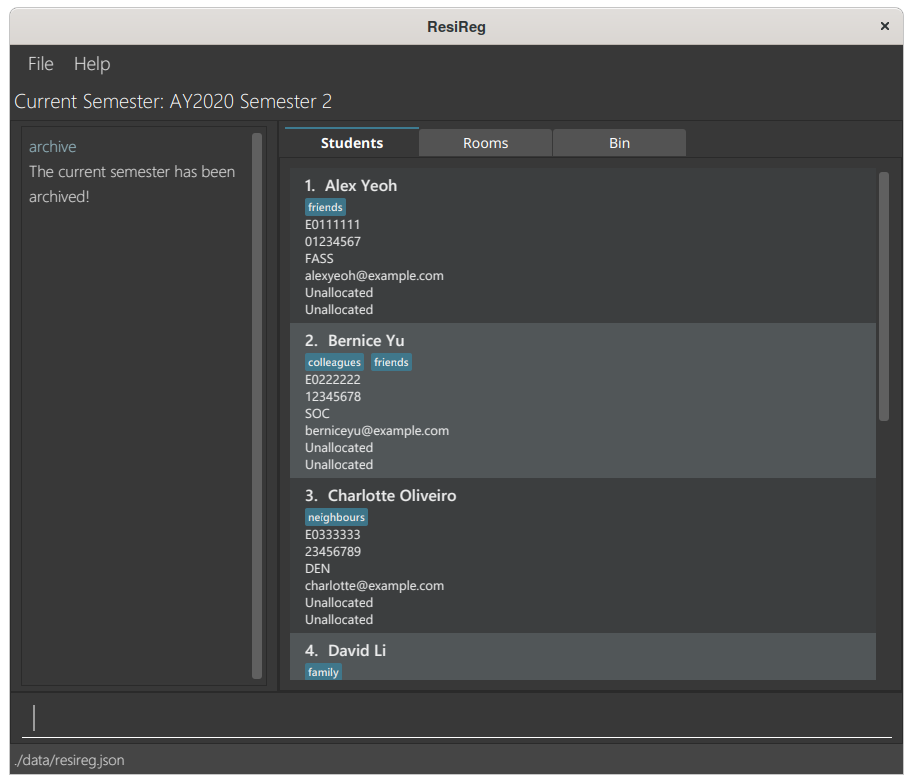
archive command will reset and restore the state of the previous semester, but the created archival folder will not be deleted. Any changes followed by another archive command will overwrite the contents of that folder.
Student Management
ResiReg allows you to manage students in the Residential College.
Listing all students : students
Shows a list of all students in ResiReg, optionally filtered by some parameters.
Format: students [n/<name>] [p/<phone>] [e/<email>] [f/<faculty] [i/<student_id>]
-
nameis matched case-insensitively and partially (i.e partial matches appear) -
phone,email,facultyandstudent_idare matched exactly, and must satisfy constraints listed in theadd-studentcommand - If no parameters are given, all students are shown.
- Students can be filtered by multiple criteria. See the section below for some examples.
Examples:
-
studentsswitches to the Students tab if it is not already selected, and shows the list of students on the right pane. -
students n/alexswitches to the Students tab if it is not already selected, and shows the list of students matching the name “alex” case-insensitively, on the right pane. -
students n/Alexswitches to the Students tab if it is not already selected, and shows the list of students with names containing “Alex” on the right pane. -
students n/char f/LAWswitches to the Students tab if it is not already selected, and shows the list of students with names containing “char” and belonging to the “LAW” faculty on the right pane.
n/ parameter is case-insensitive.
Adding a student : add-student
Adds a student to ResiReg. The following student details are stored: name, student ID, phone, email, faculty, and optionally, tags.
Format: add-student n/<student_name> i/<student_id> p/<phone_no> e/<email> f/<faculty> [tag/<tag_name>]...
- The student ID must be an alphanumeric string, starting with
EOand ending with 6 digits. It must be unique (no two students in ResiReg can share the same student ID). Otherwise, an error message is displayed accordingly. - The phone number should be exactly 8 digits
- The faculty should be a case-sensitive code. Refer to the following list for the faculty codes and their corresponding faculty names
-
FASS(Arts and Social Sciences) -
BIZ(Business) -
SOC(Computing) -
CLE(Continuing & Lifelong Education) -
DEN(Dentistry) -
SDE(Design & Environment) -
DNUS(Duke-NUS) -
ENG(Engineering) -
ISE(Integrative Sciences & Engineering) -
LAW(Law) -
MED(Medicine) -
MUS(Music) -
PH(Public Health) -
PP(Public Policy) -
FOS(Science) -
USP(University Scholars Programme) -
YNUS(Yale-NUS)
-
- The pairs of type-prefixes and data (eg.
n/<student_name>) may given be in any order. - The student will not be added if some pieces of information are missing. An error message will be displayed instead.
Examples:
-
add-student n/Jet New i/E0407889 p/82462157 e/jn@u.nus.edu f/SOCsuccessfully creates a new student named Jet New whose student ID is E0407889, phone number is 82462157, email is jn@u.nus.edu, and faculty is Computing (SOC). -
add-student n/Jet New i/E0407889 e/jn@u.nus.eduprompts the user with the following error message (because the faculty field is missing):Invalid command format! add-student: Adds a student to ResiReg.Parameters: n/NAME i/STUDENT_ID p/PHONE e/EMAIL f/FACULTY [tag/TAG]...Example: add-student n/John Doe s/E0123456 p/98765432e/ johndoe@u.nus.edu f/FASS
Editing a student : edit-student
Edits an existing student in ResiReg.
Format: edit-student <index> [n/<student_name>] [i/<student_id>] [p/<8_digit_phone_no>] [e/<email>] [f/<faculty>] [tag/<tag_name>]…
- Edits the person at the specified
index. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed student list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- All inputs must satisfy the constraints listed for the
edit-studentcommand - Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the student will be removed i.e adding of tags is not cumulative.
- You can remove all of the student’s tags by typing
tag/without specifying any tags after it.
Examples:
-
edit-student 1 p/82462157 e/johnd@comp.nus.edu.sgEdits the phone number and email address of the first student to be82462157andjohnd@comp.nus.edu.sgrespectively. -
edit-student 2 n/Alpha Queue tag/Edits the name of the 2nd student to beAlpha Queueand clears all existing tags.
Deleting a student : delete-student
Deletes the specified student from ResiReg.
Format: delete-student <index>
- Deletes the student at the specified
index, and moves the student to the bin. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed student list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
studentsfollowed bydelete-student 2deletes the 2nd student in ResiReg. -
students n/Royfollowed bydelete-student 1deletes the 1st student (if any) in the results of thestudentscommand.
General
ResiReg has many general features such as Command Line Interface (CLI) sugar and a recycling bin for more efficient usage by experienced users.
Listing all bin items : bin
Shows a list of all bin items in ResiReg.
Format: bin
-
binswitches to the Bin tab if it is not already selected. - If additional text is supplied after
bin, e.g.bin ,orbin dnno error message is shown. (rationale: to prevent user typos from interfering with a clear intention of viewing the bin list)
Examples: bin
Restoring a bin item : restore
Restores an existing bin item in ResiReg.
Format: restore <index>
- Restores the bin item at the specified
indexto the list it was originally deleted from (e.g. student list). The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed bin item list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
restore 1restores the first bin item in the list, to its original list.
Set bin expiry time : set-bin-expiry
Sets the amount of time (in days) that bin items stay in the bin before they are permanently removed.
Format: set-bin-expiry <number_of_days>
-
number_of_daysmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
set-bin-expiry 20sets all bin items to be permanently removed 20 days after their deletion.
Listing all aliases : aliases
Shows the list of aliases and their corresponding command words currently in ResiReg. An alias is a user-defined term that can be used interchangeably with a command word.
Format: aliases
- If additional text is supplied after
aliases, e.g.aliases ,oraliases dnno error message is shown. (rationale: to prevent user typos from interfering with clear intention of viewing the alias list)
Example: aliases
Adding an alias : alias
Adds an alias for a command word to ResiReg.
Format: alias c/<command_word> a/<alias_term>
-
command_wordmust exactly match one of the command words listed by thehelpcommand. -
alias_termcannot be an existing command word, or an existing alias.
Examples:
-
alias c/set-bin-expiry a/sbadds an aliassbfor theset-bin-expirycommand. Henceforth,sbandset-bin-expirycommand will have the same effect -
alias c/rooms a/radds an aliasrfor theroomscommand. Henceforth,randroomscommand will have the same effect. Note that filtering flags such as--allocatedand--vacantremain unchanged.
Deleting an alias : dealias
Deletes an alias for a command word in ResiReg.
Format: dealias c/<command_word> a/<alias_term>
- Both
command_wordandalias_termmust exactly match one of the command word-alias pairs listed by thealiasescommand.
Examples:
-
dealias c/set-bin-expiry a/sbremoves the aliassbfor theset-bin-expirycommand. Henceforth, typingsbwill lead to an error message forUnknown command.
Asking for help as a first time user : help
Shows a list of all available commands and their purpose to understand the usage of the commands.
Format: help
- Lists all user commands and their purpose.
- Also includes a link to this User Guide, so that the user can access further details.
Examples:
Commands available:
add-room: Adds a room to ResiReg.
add-student: Adds a student to ResiReg.
allocate: Allocates a student to a room.
clear: Clears list of students.
...other commands...
You can also refer to our user guide at: https://ay2021s1-cs2103-t16-3.github.io/tp/UserGuide.html
Checking the syntax for a command: help
Shows the purpose, syntax, and parameters of a command if you need to use the command but are unsure of its syntax.
Format: help <command_word> or <alias_term>
-
command_wordif supplied, should exactly match one of the command words listed by thehelpcommand -
aliasif supplied, should exactly match one of the aliases listed by thealiasescommand
Examples:
help rooms
Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries (students, rooms, allocations and bin items) from ResiReg.
Format: clear
- Additional arguments passed to the command are ignored.
clear will not be sent to the bin, since this command is designed to let you start using ResiReg on a clean slate. Use with care!
Undo previous command : undo
Restores the address book to the previous state where a modifying command was executed.
Redo previous undo command : redo
Reverses the most recent undo command.
undo and redo support the undoing and redoing respectively of commands
that change the state of ResiReg, which comprises of: students, rooms, allocations, semesters and bin items.
List previously entered nonempty commands : history
Lists all nonempty commands that were previously entered in chronological order. A positive integer n is also listed for each command, in front of it and separated by a tab. This integer specifies that the command is the nth command to be entered.
Exiting ResiReg : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
View students and rooms side by side: toggle-split
While allocating rooms to students, it is probably easier to view rooms and students at the same time. If the rooms and students tabs are currently separate, toggle-split will merge the students and rooms tab into 1 tab that shows them side by side, which is shown in the image below. You can use the rooms or students commands to switch to the combined tab as usual.
Format: toggle-split
toggle-split will cause the application to switch to the combined students and rooms tab, regardless of what tab you previously had open.
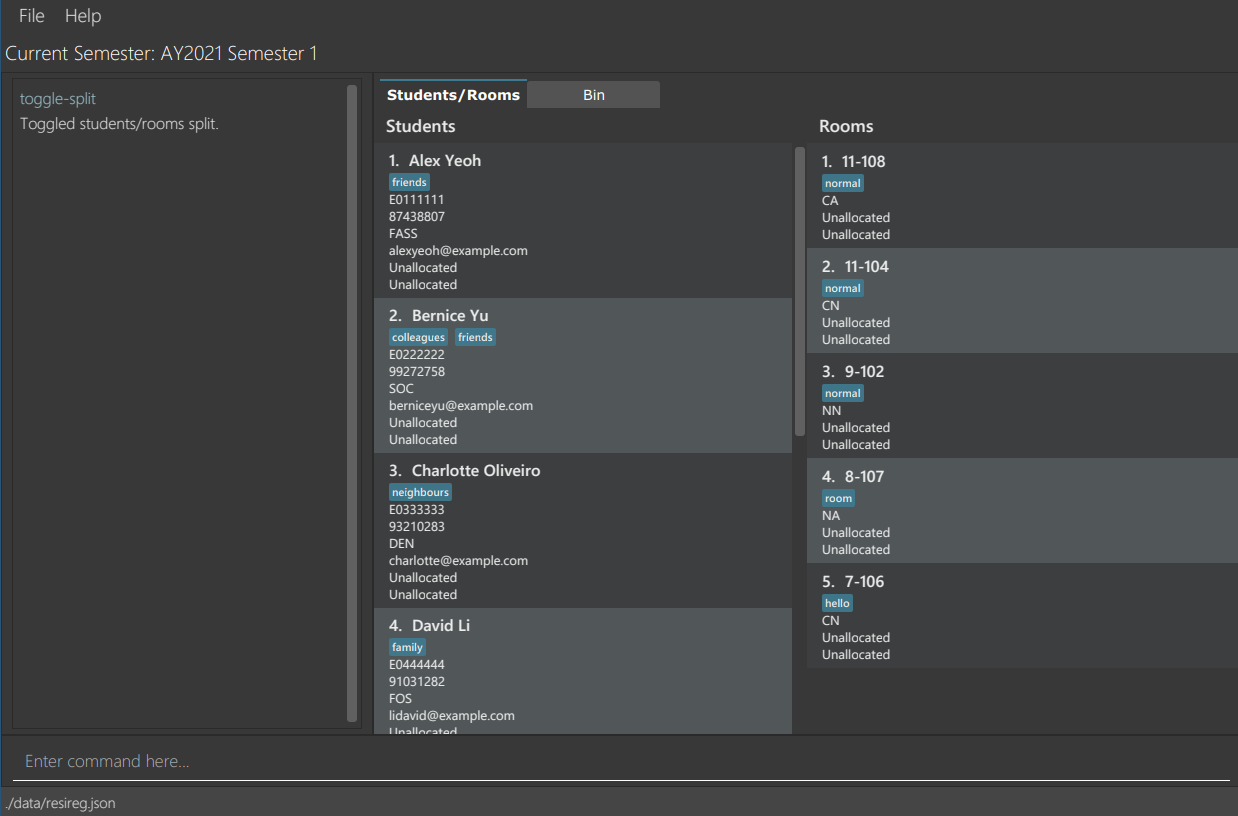
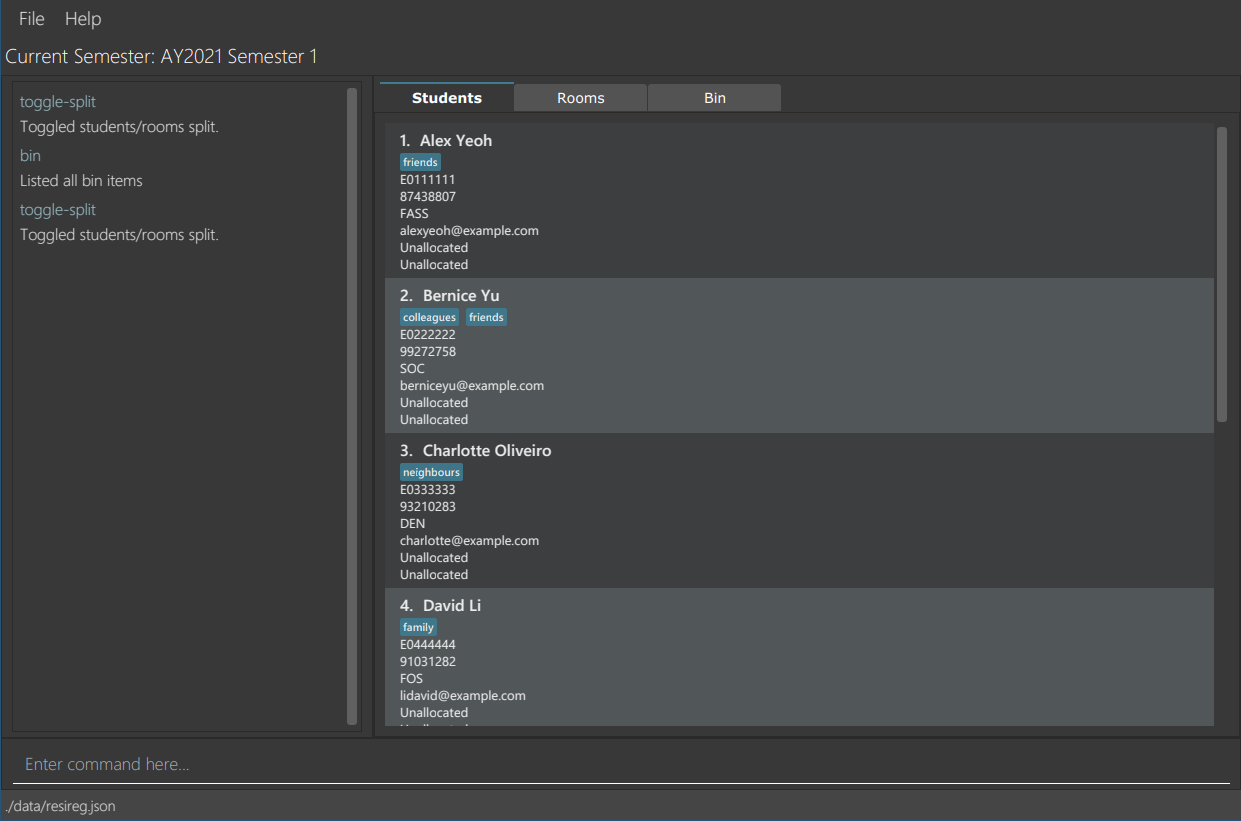
View students and rooms in separate tabs: toggle-split
If the rooms and students tab are currently combined, toggle-split will separate them into 2 separate tabs, as shown below.
Format: toggle-split
toggle-split will cause the application to switch to the students tab, regardless of what tab you previously had open.
FAQ
Where do I get help?
Just type in the help command!
How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
- Download the JAR file (
resireg.jar) on your new computer. - Navigate to where the JAR file is.
- Double click on
resireg.jar. - Delete the
resireg.jsonfile in the folder. - Copy over the
resireg.jsonfile residing in your previous ResiReg home folder that contains data of your previous ResiReg session.
Command Summary
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| list rooms |
rooms [--allocated or --vacant] [fl/<floor>] [n/<room_number>] [t/<room_type>] e.g.rooms or rooms --allocated fl/11
|
| add room |
add-room fl/<floor> n/<room_number> t/<room_type> [tag/<tag_name>]... e.g.add-room fl/11 n/101 t/CN
|
| edit room |
edit-room <index> [fl/<floor>] [n/<room_number>] [t/<room_type>] [tag/<tag_name>]... e.g.edit-room 1 n/100
|
| delete room |
delete-room <index> e.g.delete-room 1
|
| allocate room |
allocate si/<student_index> ri/<room_index> e.g. allocate si/1 ri/1
|
| deallocate room |
deallocate si/<student_index> e.g. deallocate si/1
|
| edit allocation |
reallocate si/<student_index> ri/<room_index> e.g. reallocate si/1 ri/2
|
| list students | students |
| add student |
add-student n/<name> i/<student_id> p/<8_digit_phone_no> e/<email> f/<faculty> [tag/<tag_name>]... e.g.add-student n/Jet New i/E0407889 p/82462157 e/jn@u.nus.edu f/SOC
|
| edit student |
edit-student <index> [n/<name>] [i/<student_id>] [p/<8_digit_phone_no>] [e/<email>] [f/<faculty>] [tag/<tag_name>]… e.g.edit 1 n/Jet New
|
| find students |
students [n/<name>] [p/<phone>] [e/<email>] [f/<faculty] [i/<student_id>] e.g. students n/dameeth
|
| delete student |
delete-student <index> e.g.delete 2
|
| list bin items | bin |
| restore bin item |
restore <index> e.g. restore 2
|
| set bin expiry time |
set-bin-expiry <number_of_days> e.g. set-bin-expiry 30
|
| list aliases | aliases |
| add alias |
alias c/<command_word> a/<alias_term> e.g. alias c/rooms a/r
|
| delete alias |
dealias c/<command_word> a/<alias_term> e.g. alias c/rooms a/r
|
| help |
help [<command_word> or <alias_term]e.g.helporhelp roomsorhelp r
|
| archive semester | archive |
| clear | clear |
| exit | exit |
| toggle between viewing rooms and students separately or together | toggle-split |